2025-07-14
In today’s world of advanced information technology, it is important to protect sensitive electronic devices from interference. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a common problem that can cause critical system failures, data loss, or even catastrophic failures. This is where EMI shielding comes in handy.
Metal mesh shielding film uses ultra-fine copper metal mesh technology. It has the advantages of high transmittance, extremely low resistance and excellent bending flexibility and is widely regarded as an ideal product and solution. Let’s take a deeper look at it today.
Radio wave reflection occurs when an incoming electromagnetic (EM) wave encounters a conductive surface and is bounced back rather than transmitted through. At the interface, free electrons in the conductor respond to the incident wave by generating secondary fields that oppose and reflect the original energy. In EMI shielding, maximizing this reflection prevents harmful radio‑frequency signals from penetrating or escaping an enclosed space.
– Composition: EM waves consist of oscillating electric (E) and magnetic (H) fields, oriented perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation.
– Units: Electric field strength is measured in volts per meter (V/m); magnetic field strength in milligauss (mG) or amperes per meter (A/m).
– Propagation: These waves travel at the speed of light in free space and can carry information (e.g., radio, Wi‑Fi) or act as unwanted noise.
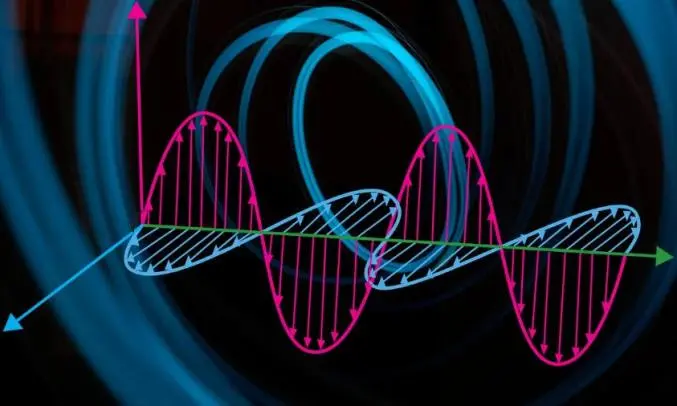

EMI shielding uses conductive or magnetic barriers to reduce the intensity of electromagnetic fields within a given volume. Its goals are:
– Containment: Prevent internal EM sources from radiating outward.
– Exclusion: Stop external EM noise from entering sensitive areas.
By leveraging radio wave reflection, shielding materials redirect energy away from protected devices, ensuring electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) across systems.
– Conducted EMI: Travels along conductive paths—power lines, signal cables—and is typically mitigated by grounding high‑conductivity shields (e.g., copper, aluminum).
– Radiated EMI: Propagates through the air as radio waves. Effective shielding relies on reflection and absorption via enclosures or coatings.
– Capacitive EMI: Results from unintended coupling between conductors at different potentials, often suppressed by inserting a grounded shield between components.
– Narrow‑band EMI: Occurs at specific frequencies (e.g., radio broadcasts). Custom shields can target these bands for optimized attenuation.
– Wide‑band EMI: Spans a broad frequency range (e.g., digital electronics). Requires comprehensive shielding strategies that combine reflection, absorption, and multiple‑reflection attenuation.
Shielding effectiveness (SE) is quantified in decibels (dB), representing the ratio of field strength before and after shielding:
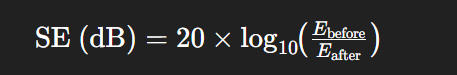
| SE (dB) | Attenuation | % Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 10× | 90% |
| 40 | 100× | 99% |
| 60 | 1,000× | 99.9% |
| 80 | 10,000× | 99.99% |
| 100 | 100,000× | 99.999% |
Higher dB values indicate stronger radio wave reflection and absorption—crucial for meeting stringent EMC standards.
Copper metal‑mesh EMI shielding films combine multiple reflection and absorption mechanisms:
– Primary Reflection: Incident waves induce opposing currents in the copper grid, reflecting most of the incoming energy.
– Multiple‑Reflection Attenuation: Waves entering the mesh’s pores undergo repeated reflections between grid lines, further reducing transmitted energy.
– Absorption: Any residual wave energy is dissipated as heat within the conductive network.
A micro‑scale grid—often with line widths under 10 µm—balances optical transparency with low sheet resistance, making it ideal for displays, windows, and other see‑through applications.

| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Transparency | Micron‑scale lines minimize light blockage—ideal for displays and glazing. |
| Low Sheet Resistance | Ensures strong reflection of high‑frequency radio waves. |
| Moiré‑Free Design | Irregular grid patterns prevent interference patterns in adjacent screens. |
| Flexibility | PET, COP, or PC substrates allow bending and stretching without damage. |
| Customizable | Grid pitch and substrate selection tailored to specific frequency bands. |
These properties make copper metal‑mesh films a top choice for modern EMI challenges.
The rollout of 5G accelerates demand for robust EMI shielding across:
– Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, AR/VR headsets require edge‑to‑edge transparent shields.
– Automotive: Electric and autonomous vehicles depend on reliable sensor and communication performance.
– Medical Devices: Wearables and diagnostic equipment demand high EMC to ensure patient safety.
– IoT & Industrial: Smart sensors and machinery controllers operate in EMI‑rich environments.
By maximizing radio wave reflection, metal‑mesh films safeguard critical electronics while preserving aesthetics and functionality.
Radio wave reflection lies at the core of effective EMI shielding. Ultra‑fine copper metal‑mesh films deliver exceptional transparency, conductivity, and flexibility—meeting the dual demands of modern electronics and EMI compliance. As technology evolves in the 5G and IoT age, these films will continue to play a pivotal role in ensuring electromagnetic compatibility across industries.
Interested in partnering on a custom EMI shielding solution? Contact us today to explore how our advanced metal‑mesh films can protect your next‑generation devices.